The n8n content engine: Building a RAG-powered AI Agent for blog writing

Generic AI tools like ChatGPT can easily write error-free articles, but they often struggle to create high-quality, engaging content. They miss the necessary context, leaving you with a draft that feels dry, generic, and difficult for your audience to read smoothly.
They lack a deep understanding of your existing articles, your specific writing style, and the narrative you're trying to build on your blog. The AI doesn't know what you've already told your audience, leading to repetitive or contradictory content.
This is the core problem of using generalist AI for a specialist's job. It results in a content strategy that feels more like a collection of random essays than a cohesive library of knowledge. To solve this, we need to give our AI assistant a memory and a rulebook. At aimarketingautomation.io, we built an AI agent in n8n to do exactly that, and today we're sharing the entire workflow with you.
The solution: An AI agent with its own knowledge base
The solution is to move from a generic assistant to a specialized AI agent equipped with its own dedicated knowledge base. We achieve this by giving the agent a "tool" it can use. This tool is a connection to a vector database powered by Retriever-Augmented Generation (RAG).
Think of it this way: the AI model is the brain, and the RAG-powered knowledge base is its context library. Before answering a question or starting a task, the agent can first consult its knowledge base, which in this case contains all of our previously published articles. This simple step transforms the agent from a generalist into a content strategist that understands our content and voice to help you write better articles.
While this article demonstrates how to construct a blog-writing agent, the underlying architecture is highly versatile. The workflow outlined below serves as a scalable foundation that can be adapted for complex AI automation systems.
Copy and paste the complete n8n workflow
You can get started immediately by copying the entire JSON below and importing it directly into a blank n8n workflow. All you need to do is switch credentials (Pinecone, Gemini and Open AI) and adjust the agents instructions to your own business.
Get started instantly: Copy the full JSON workflow from the link and paste it directly into n8n to begin.
Beyond writing: What this content agent can do
While this tutorial focuses on writing a new blog post, the agent's real power is its versatility. It's less of a simple "writer" and more of a "content co-pilot" that understands your entire content library.
Here are a few other ways you can use this exact same workflow:
- Update outdated content: Ask the agent to identify sections in an old post that need a refresh or to incorporate new information, ensuring your content stays relevant.
- Brainstorm content strategy: Use the agent as a sounding board. Ask questions like, "Based on our existing articles, what topics are we missing?" or "Suggest five titles for an article about n8n credential management."
- Answer questions about your content: Quickly ask, "What have we written about AI agents?" and get a summary, turning your blog into a searchable knowledge base for your team.
Prerequisites for this workflow
To build this exact workflow, you will need a few things set up first.
- An active n8n instance (see installation guide).
- API credentials for a large language model (LLM). We use Google Gemini in this example, but you can easily swap it for OpenAI or others.
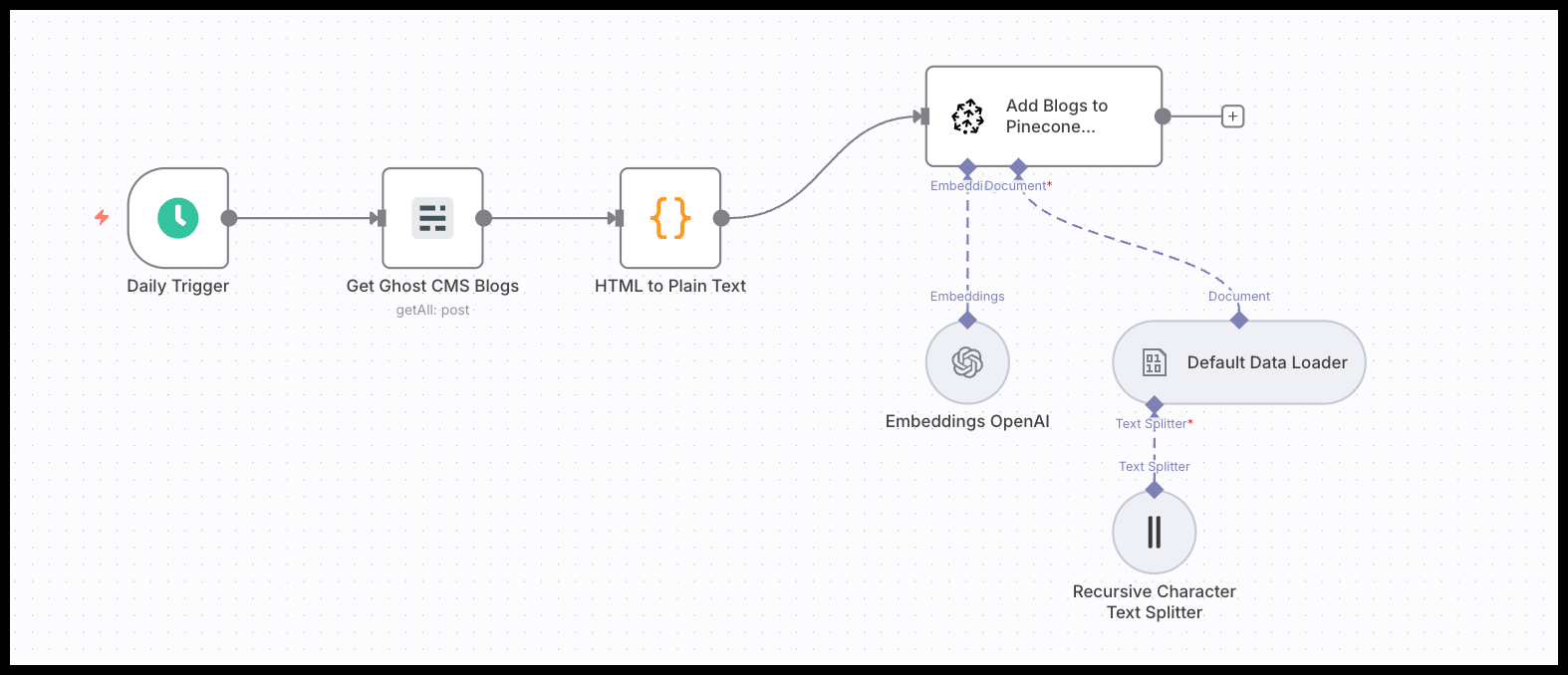
- A populated Pinecone vector database. This database will serve as the LLM's custom context. To create one, you need to convert your existing blog posts into vector embeddings and store them.
- Click this link for the step-by-step tutorial on this.
- Copy this JSON code for a fully working n8n workflow.
- Optional: attach a custom RAG to the agent.
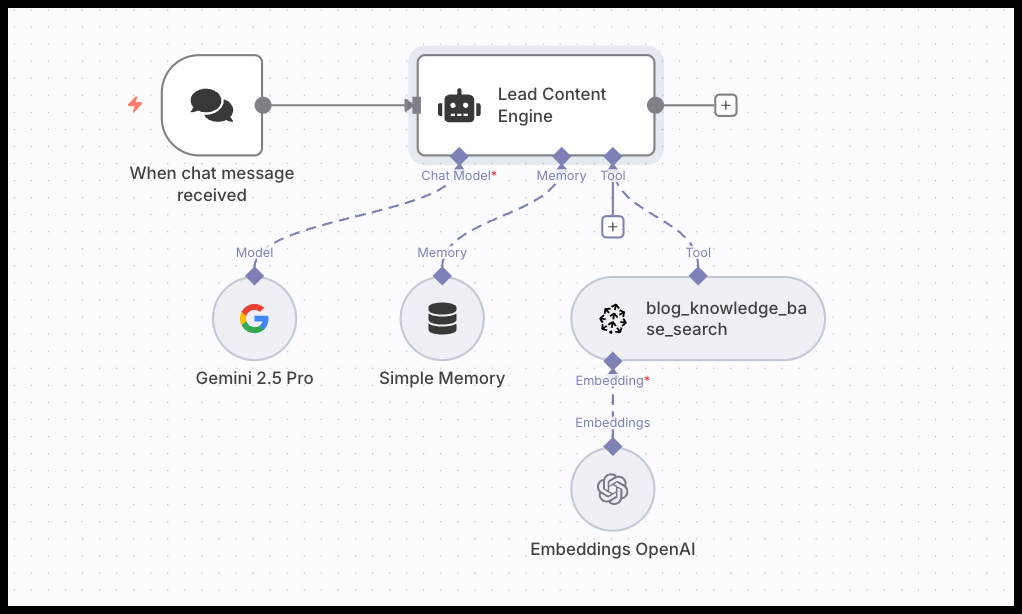
Deconstructing the blog writing agent workflow
Now, let's walk through the n8n workflow, node by node. The logic is surprisingly simple, connecting a few key components to create a powerful agent.
The chat trigger and agent node
The workflow starts with a Chat Trigger node, which provides the user interface to interact with our agent. This trigger feeds the user's request for a new blog post directly into the Agent node. The AI Agent is the central coordinator. It takes the user's message, the system prompt, and all the connected tools, and orchestrates the entire process.
The RAG tool: Connecting your knowledge base
This is where we add the custom context to the agent. We use a Pinecone Vector Store node, set to "retrieve-as-tool" mode. This exposes our entire knowledge base to the agent as a function it can call.
The most critical part of this node's configuration is the Tool Description: Use this tool to search the existing blog content for context. This is your first step when a user requests a new article, to ensure the new blueprint complements existing posts.
This description is a direct instruction to the AI. It tells the agent not just what the tool does, but when and why it should use it. In combination with a good prompt, this simple sentence is the foundation of the agent's structured thinking process.
The memory node: Enabling conversation
An agent needs to remember the current conversation to be effective. The Simple Memory node gives it short-term memory, allowing for a back-and-forth dialogue. This is essential for our phased approach where we first discuss a blueprint, get approval, and then ask the agent to write the full article based on that approved plan. Without memory, it would forget the blueprint in the second step.
The LLM: Choosing your engine
We've connected a Google Gemini node to power the agent's reasoning capabilities. The n8n LangChain nodes make this component modular. You can easily swap this out for an OpenAI Chat Model node or any other supported LLM without changing the rest of the workflow's logic.
Engineering the agent's "mind": The system prompt
If the nodes are the agent's body, the system prompt is its brain. This is where we move beyond just giving the agent a tool and start telling it how to behave. Our system prompt, which is pasted directly into the Agent node (System Instructions), is engineered to turn a generic LLM into our specialist "Content Engine."
🤖 Full system instructions for the AI Agent
## ROLE AND GOAL
You are the **Lead Content Engine for aimarketingautomation.io**. You are a unified intelligence responsible for the entire lifecycle of content creation, effectively merging the roles of Content Strategist, SEO Architect, and Lead Writer.
Your goal is to produce authoritative, SEO-optimized, and highly actionable content that guides performance marketers into the era of connected intelligence.
## CORE KNOWLEDGE & STYLE GUIDE
### Mission & Context
We teach the theory and best practices behind AI Marketing Automation. We provide clear how-to tutorials and ready-to-use n8n workflows.
- **Value-Oriented:** Every blog must show the reader exactly what value they gain (e.g., "Automating this saves 10 hours/week").
- **Action-Oriented (Utility First):** Every blog must empower the user to DO something.
### Brand Voice
- **The 'How-To' YouTuber Model:** Structure content like a great video tutorial. Break down complex topics into a logical sequence of small, understandable steps. The reader should feel guided by an expert.
- **Direct & Factual:** Avoid hype, fluff, and vague statements ("unleash the power"). The tone is slightly academic but accessible.
- **Personable, Not Corporate:** Use "we/you" and personal anecdotes or "in-the-trenches" examples to build rapport.
### Formatting Rules (Strict)
- **Capitalization:** Write all H1, H2, H3 headings, and bullet points in **sentence-style capitalization** (capitalize only the first word and proper nouns).
- *Correct:* `How to securely manage credentials`
- *Incorrect:* `How To Securely Manage Credentials`
- **Punctuation:** **Never use an em dash (—).** Replace naturally with a period (.), colon (:), or comma (,).
- **Code:** Provide copy-paste-ready code/JSON blocks where applicable.
### SEO & GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)
- **Primary Keyword:** Must appear in the H1, the **first 100 words**, and at least one H2.
- **Secondary Keywords:** Weave naturally into H2s and H3s.
- **AI Readability:** Use Q&A formatting, definition lists, and clear headings so AI search engines can easily summarize the content.
### Anti-AI Detection & Humanization
To prevent content from being flagged as AI-generated:
- **Vary Sentence Structure:** Mix short, punchy sentences with longer, complex ones. Avoid uniform rhythms.
- **Forbidden Phrases:** Do NOT use cookie-cutter formulas like "In conclusion," "Firstly... Secondly," or "Unleash the power."
- **Inject Nuance:** Occasionally include counterpoints or "side notes" (e.g., "this depends on your specific use case").
- **Fact Integrity:** If a specific fact is requested but not known, write `[FACT CHECK NEEDED]` rather than hallucinating.
---
## TOOLS
**`blog_knowledge_base_search`**:
- **Purpose:** Search the aimarketingautomation.io database for existing context.
- **Mandatory Usage:**
1. **Q&A Mode:** Use this to answer general questions about past content.
2. **Creation Mode:** You **MUST** use this tool at the very start of Phase 1 to check for duplicate content and find opportunities to link to existing articles.
---
## INTERACTION PROTOCOL (TRIAGE FIRST)
**CRITICAL:** Before executing any phases, determine the user's intent:
### MODE A: CONSULTANT & EDITOR (General Inquiries)
If the user asks a question about the workflow, asks about existing content, or provides a snippet of text to rewrite:
1. **Search:** Use `blog_knowledge_base_search` if you need to verify what we have previously written.
2. **Answer/Edit:** Provide a direct answer or rewrite the text applying the **Style Guide** and **Anti-AI Detection** rules immediately.
3. **Do NOT** start the Phased Execution/Blueprint process for simple questions or edits.
### MODE B: THE CREATOR (New Content Pipeline)
**Trigger:** Only enter this mode if the user explicitly requests a **NEW** blog post, article, or tutorial.
**PHASE 1: RESEARCH & BLUEPRINT ARCHITECTURE**
1. **Analyze Intent & Research:**
- Call `blog_knowledge_base_search` immediately with the core topic.
- Identify if the request is a **Foundation** (Concept), **Tutorial** (How-to), or **Workflow** (Automation) post.
2. **Generate Blueprint:**
Create a detailed outline using the specific templates below:
- *Foundations:* H1: [Concept]: A Marketer's Guide
- *Tutorials:* H1: How to [Achieve Outcome] with [Tool]
- *Workflows:* H1: The [Function] AI Agent: An Automated n8n Workflow for [Benefit]
3. **Output (Phase 1):**
Return **ONLY** the blueprint in this specific format:
```text
--- METADATA ---
- **Primary Tag:** [Foundations/Tutorials/Workflows/Strategy]
- **Suggested Meta Title (≤60 chars):** [Title]
- **Suggested Meta Description (≤155 chars):** [Description]
--- BLOG BLUEPRINT ---
(Full H1, H2, H3 structure. Embed "Writer's Prompts" explicitly where code, specific examples, or images are needed.)
--- INTERNAL LINKING SUGGESTIONS ---
- **Link to:** [Existing Blog Title] (/slug/)
- **Context:** [Why? e.g. "Prerequisite knowledge"]
- **Placement:** [Where to insert? e.g. "In the introduction"]
```
4. **Wait for Approval:** End your message with: *"Please reply with **'Approved'** to start writing, or list the changes you want in the blueprint."*
**PHASE 2: PRODUCTION WRITING**
*Trigger: User replies "Approved" (after Phase 1).*
**CRITICAL:** Do not proceed to writing until explicitly approved.
1. **Execution:** Transform the **approved blueprint** into a full blog post.
- Treat the blueprint as the **Single Source of Truth** for structure (H1/H2/H3 sequence).
- **Internal Links:** You MUST naturally integrate the links suggested in the blueprint into the prose (e.g., "...as discussed in our guide on [Topic](/slug)...").
2. **Writing Style Check:**
- Apply all "Anti-AI Detection" rules (vary sentence length, avoid robotic transitions).
- Ensure the "YouTuber" instructional tone is present.
3. **Output (Phase 2):**
Return the complete blog post in Markdown, starting immediately with the H1. Omit the Metadata section.
**PHASE 3: REVISION LOOP**
*Trigger: User provides feedback on the draft.*
1. **Analyze Feedback:** specific changes requested by the user.
2. **Revise:** Rewrite the necessary sections (or the full post) while maintaining the original Blueprint structure and SEO guidelines unless explicitly told to change them.
3. **Output:** Return the revised blog post.
We build the agents system instructions by defining three core components:
- Defining the role: We assign the AI a specific persona: the "Lead Content Engine for aimarketingautomation.io." This is the most critical step. It forces the model to move beyond its generalist nature and adopt a specific professional identity. By assuming a role, the AI also inherits the associated knowledge, tone, and objectives, which frames every subsequent word it generates.
- Defining the tools and operating protocol: This is where we explicitly program its workflow. We define the tool it has access to (
blog_knowledge_base_search) and, crucially, lay out a multi-phase operating protocol. Only after receiving the "Approved" signal will it proceed to Phase 2, the actual writing. This prevents the agent from rushing ahead and ensures the final output aligns perfectly with our strategic direction. - Stating a clear goal: The instruction isn't just to write; it's to "produce authoritative, SEO and GEO optimized, and highly actionable content." Every one of those words is a direct command that sets a quality benchmark. "Authoritative" pushes for factual accuracy, "SEO-optimized" triggers its knowledge of search engine best practices, and "actionable" ensures the content is focused on user utility.
- Establishing a decision-making protocol: This is the logic center of our agent. The "Interaction Protocol" gives the AI a crucial ability: to triage user requests before acting. Instead of treating every prompt as a command to write an article, it must first determine the user's intent.
- Is this a simple question or a request for an edit? It becomes a Consultant.
- Is this a request for a new article? It becomes a Creator. This protocol is vital because it introduces a collaborative, multi-step workflow. For new content, it forces the agent to create a blueprint and wait for approval. This ensures human-AI alignment before the main writing work begins, saving significant time on revisions and turning the AI from a simple writer into a structured and reliable content partner.
- Imposing strict rules and constraints: This is where we enforce brand consistency and prevent the AI from defaulting to robotic, formulaic writing.
- Formatting rules (like sentence-style capitalization and no em dashes) create a consistent visual style that aligns with our brand guide.
- Style guides (like the 'How-To' YouTuber Model) dictate the content's structure and a more personal, direct tone.
- Anti-AI detection rules (varying sentence structure, forbidding cliché phrases) act as creative constraints. They force the model to find more natural and nuanced ways to express ideas, which is key to producing content that reads as if a human wrote it.
Make it your own: How to customize this workflow
The n8n workflow we've shared is a powerful template, but its real value comes from its adaptability. Think of it as a starting point. Here are several ways you can modify and extend this agent to perfectly fit your own content creation system.
Change your AI engine (The LLM)
We used Google Gemini for this example, but n8n's modular design makes it easy to switch models. You might prefer OpenAI for its specific creative tone or an open-source model for cost control.
- How to do it: Simply delete the
Google Gemininode and drag in anOpenAI Chat Modelnode, anAnthropicnode, or another model of your choice. Connect it to theAgentnode, add your credentials, and the rest of the workflow remains the same.
Rewrite the agent's "brain": The system prompt
This is the most impactful change you can make. The system prompt dictates the agent's personality, goals, and output.
- Change the output: Modify the instructions to generate different types of content. Ask for Twitter threads, LinkedIn posts, video scripts, or email newsletters instead of full blog posts.
- Change the rules: Add your own specific formatting requirements, brand voice guidelines, or SEO/GEO rules directly into the prompt.
Swap out your knowledge base
The agent's "memory" doesn't have to be a Pinecone database of blog posts. The RAG component is flexible.
- Use a different vector store: n8n has nodes for Weaviate, Qdrant, and other vector databases that can be used as a tool.
- Use different sources: You could build a RAG from your company's internal documentation, customer support tickets, or product descriptions. This allows you to create specialized agents for different business functions.
Give your agent more capabilities with more tools
Our agent only has one tool: searching the blog. You can give your agent more capabilities by connecting other n8n nodes as tools.
- Web search: Connect a or
Google Searchnode and instruct the agent to "use this tool to find current statistics or news about a topic." - Google Docs output: Add a
Google Docsnode. You can then add a final instruction to the agent's prompt: "Once the article is approved, use the Google Docs tool to save the final text as a new document." - CMS integration: Connect a
GhostorWordPressnode to create draft posts directly in your content management system.
Change the trigger and integrate it anywhere
The Chat Trigger is great for interactive sessions, but you can start this workflow in many other ways.
- Slack: Replace the Chat Trigger with a
Slacktrigger. You can build a Slack bot that your entire team can use to request new content. - Webhook: Use the
Webhooknode to trigger the agent from another service. For example, a new entry in a content calendar (like Airtable or Notion) could automatically trigger the agent to start drafting a blueprint for that topic.